Table 1 Synthetic methods of dicoumarols using different types of catalysts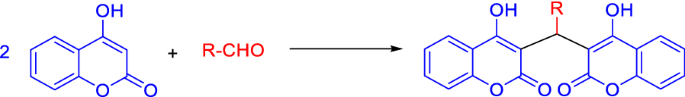

Type of catalyst | Catalyst | Conditions | Dicoumarol derivatives R (yields) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Lewis acids | I2 | I2 (10 mol%), H2O, 100 °C, 1 atm, 20–34 h | Ph (97%), 2-HOC6H4 (98%) 3-O2NC6H4 (94%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-O2NC6H4 (95%), 4-HOC6H4 (98%) 4-MeOC6H4 (99%), –CH–CH–C6H4 (92%) Furan-2-yl (93%), thiophen-2-yl (91%) Indol-3-yl (95%), 3,4-piperonyl (96%) | [45] |
MnCl2 | MnCl2 (10 mol%), H2O, 100 °C, 20–40 min | MeCH=CH– (95%), Ph (99%) 2-HOC6H4 (93%), 4-ClC6H4 (99%) 4-HOC6H4 (95%), 4-MeOC6H4 (97%) 4-O2NC6H4 (99%), furan-2-yl (96%) thiophen-2-yl (95%), indol-2-yl (94%) | [46] | |
Zn(Proline)2 | Zn(Proline)2 (5 mol%), H2O, reflux, 5–9 min | Ph (92%), 2-ClC6H4 (96%) 2-HOC6H4 (92%), 3-O2NC6H4 (93%) 4-ClC6H4 (94%), 4-HOC6H4 (96%) 3-MeO-4-HOC6H3 (91%) thiophen-2-yl (93%) 5-Me-thiophen-2-yl (92%) pyridin-4-yl (91%) | [47] | |
InCl3 | InCl3 (10 mol%), H2O, MW, 110 °C, 15–20 min | Ph (92%), 4-ClC6H4 (91%), 4-FC6H4 (93%) 4-HOC6H4 (90%), 4-MeC6H4 (85%) 4-MeOC6H4 (87%), 4-O2NC6H4 (96%) 4-HO-3-MeOC6H3 (89%) 3,4-(HO)2C6H3 (85%) 4-HO-3,5-(MeO)2C6H2 (86%) | [48] | |
Lewis and Bronsted acids | Sulfated titaniaa (TiO2/SO42−) | (TiO2/SO42−) (15%), H2O, 80 ºC, 12–30 min | H (95%), Et (88%), Ph (92%), Pr (90%) iPr (90%), Me-CH=CH– (92%) 2-HOC6H4 (95%), 2-MeOC6H4 (85%) 2-O2NC6H4 (90%), 3-BrC6H4 (91%) 3-ClC6H4 (92%), 3-HOC6H4 (84%) 3-MeOC6H4 (88%), 3-O2NC6H4 (90%) 4-BrC6H4 (94%), 4-ClC6H4 (96%) 4-HOC6H4 (96%), 4-MeC6H4 (89%) 4-MeOC6H4 (92%), 4-O2NC6H4 (88%) 4-OH-3-MeOC6H3 (89%) 3-OH-4-MeOC6H3 (85%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (90%) 3,4,5-(MeO)3C6H2 (94%) 4-BnO-3-MeOC6H2 (82%) 4-CNC6H4 (96%), 4-Me2NC6H4 (89%) Ph-CH=CH– (86%), naphthalen-1-yl (85%) Furan-2-yl (90%) | [49] |
Inorganic acid salts | B(HSO4)3 | B(HSO4)3 (0.3 equiv) (1:1, H2O–EtOH), 70 °C, 3–6 min | Ph (86%), 3-MeOC6H4 (81%) 3-O2NC6H4 (82%), 4-BrC6H4 (95%) 4-ClC6H4 (92%), 4-NCC6H4 (86%) 4-FC6H4 (88%), 4-MeC6H4 (87%) 4-MeOC6H4 (83%), 4-O2NC6H4 (98%) 4-Cl-3-O2NC6H3 (88%) | [50] |
Transition metals salts | RuCl3·nH2O | RuCl3·nH2O (5 mol%), H2O, 80 °C, 25–35 min | Et (75%), Ph (84%), 4-ClC6H4 (85%) 4-NCC6H4 (95%), 4-MeOC6H4 (92%) 3-(PhO)-C6H4 (90%), 2-Cl-6-FC6H3 (92%) 3,4-(F2)C6H3 (90%) 2-HO-3-MeOC6H3 (84%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (84%), indol-3-yl (90%) 2-O2NC6H4CH=CH– (90%) | [51] |
Ionic liquids | [bmim]BF4 | [bmim]BF4 (4 equiv) 60–70 °C, 2–3 h | Ph (84%), 3-ClC6H4 (84%) 4-BrC6H4 (87%), 4-ClC6H4 (91%) 4-MeC6H4 (83%), 4-MeOC6H4 (87%) 4-O2NC6H4 (84%), Me2CH– (77%) Ph-CH=CH– (82%), furan-2-yl (83%) pyridin-2-yl (81%) | [52] |
SO3H-functionalized ILs based on benzimidazolium cation | [PSebim][OTf]b (10 mol%), 70 °C, 2–3 h | Ph (95%), 3-BrC6H4 (94%) 3-ClC6H4 (94%), 4-BrC6H4 (95%) 4-ClC6H4 (96%), 4-MeC6H4 (93%) 4-MeOC6H4 (93%), 4-O2NC6H4 (96%) 4-(H2C=CH2)C6H4 (92%) | [53] | |
[MIM(CH2)4SO3H][HSO4] | [MIM(CH2)4SO3H] [HSO4] (15 mol%), 80 °C, 18–30 min | Ph (92%), 2-ClC6H4 (88%) 2-O2NC6H4 (86%), 3-ClC6H4 (89%) 3-O2NC6H4 (89%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-MeC6H4 (90%), 4-MeOC6H4 (89%) 4-O2NC6H4 (96%) | [54] | |
Tetramethyl guanidium acetate ([TMG][Ac]) | [TMG][Ac] (0.75 mmol), rt, 0.5–4.5 h | Ph (96%), 2-HOC6H4 (90%) 2-O2NC6H4 (92%), 3-O2NC6H4 (87%) 4-BrC6H4 (96%), 4-ClC6H4 (88%) 4-FC6H4 (93%), 4-F3CC6H4 (91%) 4-MeC6H4 (90%), 4-MeOC6H4 (86%) 4-O2NC6H4 (99%), pyridin-4-yl (87%)
(98%) | [55] | |
Choline hydroxide | ChOH (40%)c, 50 °C, 1–3 h | H (quantitative), Ph (99%) 2-HOC6H4 (99%), 2-O2NC6H4 (75%) 3-O2NC6H4 (93%), 4-BrC6H4 (94%) 4-ClC6H4 (99%), 4-FC6H4 (99%) 4-F3CC6H4 (96%), 4-HOC6H4 (94%) 4-MeC6H4 (94%), 4-MeOC6H4 (95%) 4-HO-3-MeOC6H3 (93%), furan-2-yl (98%)
| [56] | |
[P4VPy-BuSO3H]Cl-X(AlCl3)d | IL (0.07 mmol), toluene, 90 °C, 0.5–0.9 h | Ph (95%), 2-HOC6H4 (90%) 3-ClC6H4 (96%), 3-O2NC6H4 (96%) 4-ClC6H4 (93%), 4-MeC6H4 (94%) 4-MeOC6H4 (92%), 4-HOC6H4 (90%) 4-O2NC6H4 (96%), furan-2-yl (91%) Thiophen-2-yl (91%), pyridin-2-yl (91%) Ph–CH2–CH2 (92%), CH3CH2CH2– (92%) Ph-CH=CH– (93%) | [57] | |
[Dabco-H][AcO] | [Dabco-H][AcO] (10 mol%), H2O, 80 °C, 2–15 min | n-Pr (99%), Ph (98%), 2-BrC6H4 (98%) 3-BrC6H4 (98%), 4-BrC6H4 (99%) 4-ClC6H4 (99%), 4-MeC6H4 (96%) 4-MeOC6H4 (98%), 4-O2NC6H4 (99%) 2,4-Cl2C6H3 (96%), naphthalen-2-yl (99%) thiophen-2-yl (98%), furan-2-yl (98%) | [58] | |
Hnmp/ZnCl3 | (Hnmp/ZnCl3) (20 mg), 100 °C, 30–50 min | Ph (97%), 3-ClC6H4 (86%) 3-MeOC6H4 (90%), 3-O2NC6H4 (81%) 4-ClC6H4 (90%), 4-HOC6H4 (81%) 4-MeC6H4 (88%), 4-MeOC6H4 (93%) 4-O2NC6H4 (86%), 2,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (78%) pyridin-4-yl (90%) | [59] | |
Heteropoly acids (HPAs) | Phosphotungstic acid | HPA (15 mmol%), H2O, 80 °C, 14–25 min | Ph (93%), 2-ClC6H4 (95%) 2-HOC6H4 (98%), 2-O2NC6H4 (96%) 3-O2NC6H4 (94%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-FC6H5 (98%), 4-HOC6H4 (98%) 4-MeOC6H4 (99%), 4-O2NC6H4 (95%) 2,4-Cl2C6H3 (92%), 2,6-Cl2C6H3 (98%) –CH=CH–C6H4 (98%), 3,4-piperonyl (96%) Indol-3-yl (95%), thiophen-2-yl (91%) Furan-2-yl (93%), 4-F3CC6H4 (98%) 4-Me2C6H3 (90%), 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (90%) | [60] |
Phase transfer catalysts and surfactants | Tetrabutyl ammonium bromide (TBAB)e,f | TBAB (10 mol%), H2O, 100 °C | Ph (92%), 3-ClC6H4 (87%) 4-BrC6H4 (88%), 4-ClC6H4 (95%) 4-MeC6H4 (92%), 4-MeOC6H4 (84%) 4-O2NC6H4 (91%), Ph–CH=CH– (82%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (87%), Me2CH– (82%) 3,4,5-(MeO)3C6H2 (84%), piperonyl (88%) furan-2-yl (88%), pyridin-2-yl (90%) 4-(Me)2CHC6H4 (91%) | [61] |
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | SDS (20 mol%), H2O, 60 °C, 2.30–3.0 h | Ph (90%), 2-MeC6H4 (84%) 3-ClC6H4 (92%), 3-O2NC6H4 (95%) 4-BrC6H4 (91%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-FC6H4 (94%), 4-MeC6H4 (97%) 4-(Me)2NC6H4 (94%), 4-MeOC6H4 (97%) 4-O2NC6H4 (98%), 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (98%) | [62] | |
Modified glycerols | Propane-1,2,3-triyl tris(hydrogen sulfate) (PTTH) | PTTH (0.03 mol%), 80 °C, H2O, 7–10 ming or solvent-free, 5–8 min | H (80%), Ph (90%), 2-ClC6H4 (85%) 3-O2NC6H4 (95%), 4-ClC6H4 (90%) 4-HOC6H4 (85%), 4-MeC6H4 (90%) 4-MeOC6H4 (85%), 4-O2NC6H4 (95%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (85%), Ph-CH=CH– (85%) furan-2-yl (80%) | [63] |
 3-MeO-4-HOC6H3 (84%), furan-2-yl (95%)
3-MeO-4-HOC6H3 (84%), furan-2-yl (95%) 4-O2NC6H4 (89%), pyridin-4-yl (81%) (95%)
4-O2NC6H4 (89%), pyridin-4-yl (81%) (95%)